Protein Translocation Assays
Track Cellular Movement of Proteins to Multiple Membrane Compartments
The movement of proteins from the plasma membrane to endosomes, endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane, or cytoplasm to the nucleus is essential for the protein's specific biological role. When natural movements are altered by therapeutic binding, protein mutations, or abnormal signaling, undesirable consequences such as drug tolerance, unwanted side effects, therapeutic toxicity, and diseases may occur. Measuring therapeutic binding that affects translocating proteins provides insight into these adverse effects and ultimately helps to identify safer drugs.
Eurofins DiscoverX® PathHunter® protein translocation assays provide the ability to study the internalization and cellular trafficking of your protein of interest to and from different cellular compartments and analyze the pharmacological effects of therapeutics on these events. Unlike alternative methods that require specialized equipment, antibodies, or fluorescent tags, these cell-based assays are high-throughput, easy-to-use, quantitative, and highly specific and sensitive.
Product Highlights
- Simple, Homogeneous Assay – Explore protein translocation to multiple cellular compartments using an easy-to-use, non-imaging, high throughput cell-based assay platform
- Pharmacochaperone Discovery – Identify small molecule compounds that functionally rescue disease relevant mutant proteins involved in cystic fibrosis, Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and others
- Biologics Discovery – Quantify peptide and antibody-based therapeutics targeting receptors that can induce high levels of translocation
- Flexible Solutions – Create quantitative, custom cell-based assays to study the translocation of any protein (e.g., GPCRs, RTK, checkpoint receptors, nuclear proteins, ion channels, & more)
Internalization Assays
- GPCR Cell Lines and Assay Ready Kits
- Checkpoint Receptor Cell Lines
- Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) Cell Lines
Pharmacotrafficking Assays
- Pharmacochaperone trafficking assays (GPCRs, Ion Channels, and Transporters)
Translocation Assays
- Nuclear Protein Cell Lines and Assay Ready Kits
- NHR Cell Lines
PathHunter protein translocation assays are based on the proprietary Enzyme Fragment Complementation (EFC) technology to measure the movement of proteins into different cellular compartments (e.g., to the cell membrane, nucleus, or endosome).
Receptor Internalization Assay Principle
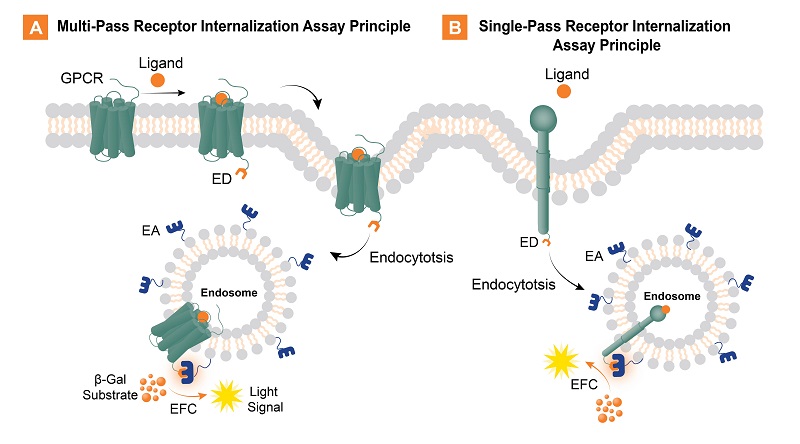
Internalization assay principles for multi- and single-pass receptors. These assays monitor the internalization of membrane receptors in an imaging and antibody-free, homogeneous (no wash) HTS-friendly assay format. A. Multi-pass receptor (e.g., GPCR) internalization assay principle showing the PathHunter total GPCR internalization assay. Refer to the GPCR Internalization Assays page for measuring activated internalization through the GPCR-β-arrestin complex. B. Single-pass receptor internalization assay principle for checkpoint receptors or receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). These assays detect membrane receptor translocation to the endosome after ligand binding for all internalization assay principles. For these two examples, the cell lines are engineered to co-express an EFC enzyme donor (ED)-tagged membrane receptor and an EFC enzyme acceptor (EA) tag localized to the endosome. A small molecule or biologic (e.g., antibody) ligand that bind the receptor-ED fusion protein leads to the internalization of the receptor to the EA-tagged endosome, forcing complementation of the two β-galactosidase (β-gal) enzyme fragments (ED and EA). The resulting functional β-gal enzyme hydrolyzes a substrate to generate a chemiluminescent signal.
Pharmacotrafficking Assay Principle
Pharmacochaperone Trafficking Assays can be used for broad pharmacological characterization and interrogation of small molecule compound function in disease processes associated with defects in membrane protein (e.g. GPCRs, ion channels, transporters) trafficking and internalization due to protein misfolding. Refer to Pharmacochaperone Trafficking Assays for the assay principle and details.
Nuclear Hormone Receptor (NHR) Translocation Assay Principle
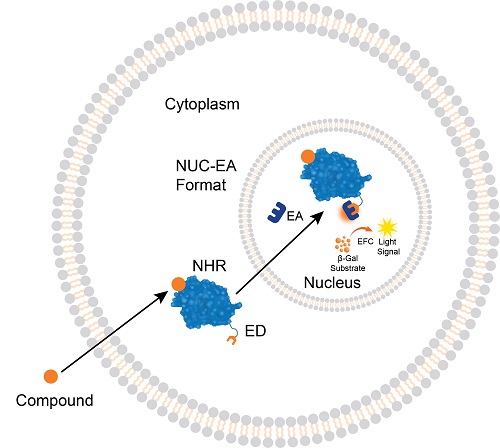
NHR translocation assays detect the binding of small molecules that trigger NHR activation and translocation into the nucleus. The cells have been engineered to express the ED fragment of the β-gal enzyme fused to the NHR (that is located in the cytoplasm) and the EA fragment localized in the nucleus. Ligand binding to the NHR induces the receptor translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, forcing the complementation of the ED and EA fragments and the formation of an active β-gal enzyme. The enzyme then hydrolyzes a substrate to generate a chemiluminescent signal that can be easily measured on any standard luminometer. Learn about NHRs on the nuclear proteins page.
Nuclear Translocation Assay Principles
Nuclear translocation assays allow for the identification, screening, lead optimization, and even safety testing of therapeutics. These assays monitor the activation or inhibition of a particular signaling pathway coupled with the movement of proteins from the cytosolic compartment to the nuclear compartment. In general, this approach enables you to create a highly specific, non-transcriptional assay for almost any protein that is known to translocate to the nucleus, such as FOXO3, NRF2, XBP1, p53, and many others. Learn about several translocation assays on the nuclear proteins and signaling pathways pages.
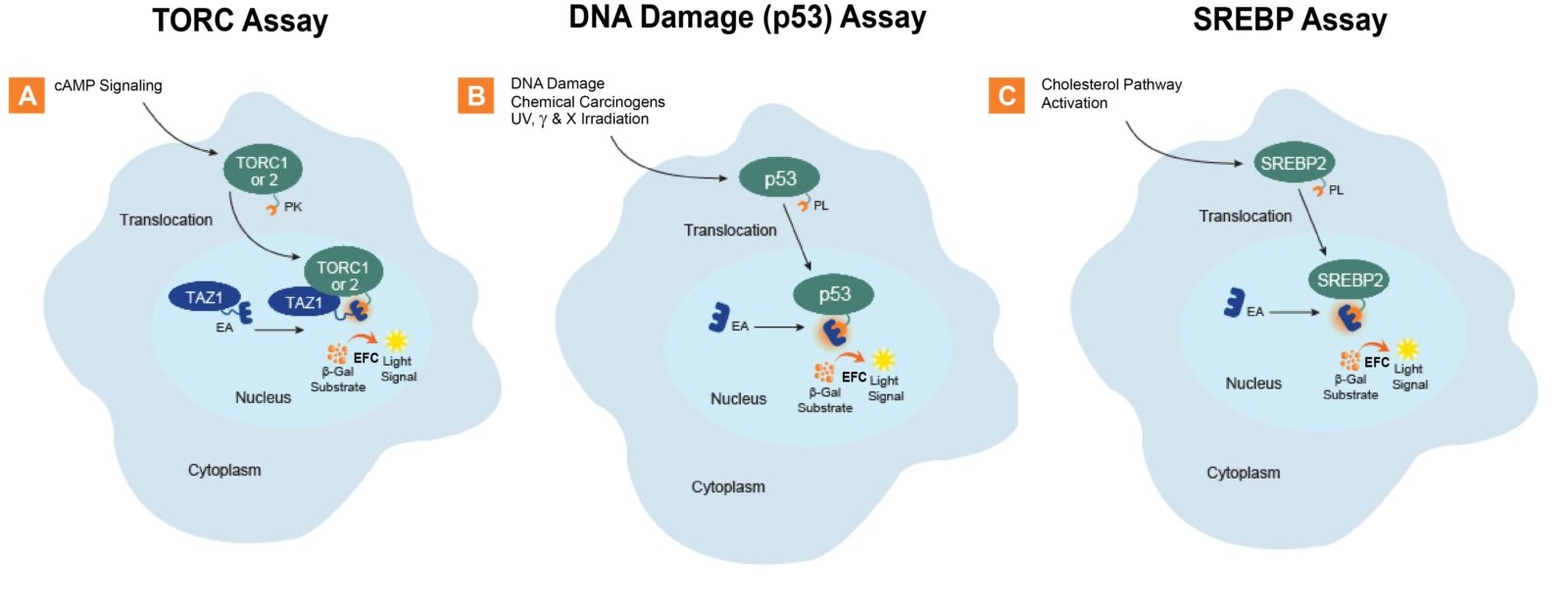
Nuclear translocation assays allow for the identification, screening, lead optimization, and safety testing of therapeutics. These assays monitor the activation or inhibition of a particular signaling pathway coupled with the movement of proteins from the cytosolic compartment to the nuclear compartment. In general, this approach enables you to create a highly specific, non-transcriptional assay for almost any protein that is known to translocate to the nucleus, such as FOXO3, NRF2, XBP1, p53 and many others. Example PathHunter signaling pathway assays shown here measure (A.) TORC1 or TORC2, (B.) p53, and (C.) SREBP2 translocation from the cytosol to the nucleus. The cell lines have been engineered to express the two complementing EFC β-galactosidase (β-gal) fragments within different cellular compartments. The translocating protein is tagged with the small EFC enzyme donor (ED) fragment, while the larger EFC enzyme acceptor (EA) fragment is located in the nucleus. Activation of the pathway by a ligand (small molecule, peptide, or biologic) triggers the ED-tagged protein that is being measured to translocate to the nucleus and complement with the EA to form a fully active β-gal enzyme. The enzyme then hydrolyzes a substrate to generate a chemiluminescent signal that can be easily measured on any standard luminescence reader.
There are several applications for translocation assays shown below. For more applications, please refer to the GPCR Internalization, Pharmacotrafficking, and Toolbox pages.
Profile Molecules that Trigger Receptor Internalization and Compare Results to Other Assay Types
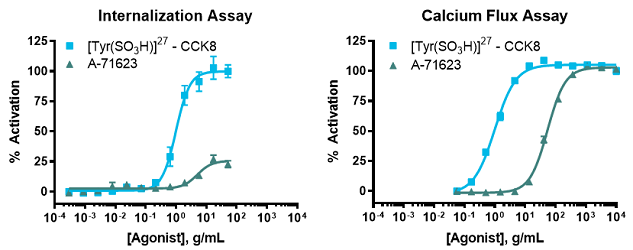
Comparing agonist profiles using the same target within internalization and calcium flux assays. Data from the PathHunter GPCR CCKAR (cholecystokin A receptor) Internalization Assay can be used for comparison to results obtained from other GPCR CCKAR Assays (β-arrestin recruitment, cAMP accumulation, or calcium flux) evaluating receptor signal activity in response to the same ligands. Combining knowledge of how ligand/compound binding affects receptor signaling events, as well as receptor localization and internalization, can provide insights into the overall effects on efficacy and safety.
Profile Molecules Using Different Assay Types to Determine Unique Pharmacologies
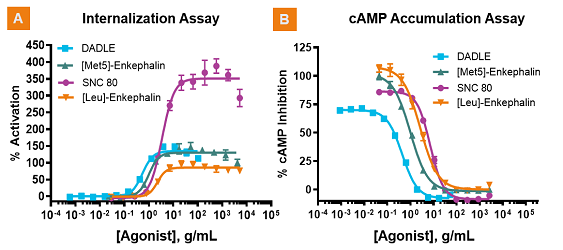
Comparing agonist profiles within different assay types and revealing unique pharmacologies. Four human δ-Opioid receptor (hDOR) agonists were characterized for their activation of receptor internalization and the inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation. Cells overexpressing the hDOR receptor in the PathHunter Activated GPCR Internalization (A.) and cAMP Hunter (B.) formats were treated with known agonists and assayed using PathHunter and HitHunter® Detection reagents respectively. For comparison, the data was normalized to [Met5]-enkephalin in potency (value set to 1) and efficacy (set to 100%). Despite similar compound potencies and efficacies based on the inhibition of cAMP accumulation in the cAMP assay, SNC-80, which is known as a strongly internalizing compound and functional antagonist is clearly defined as a super-agonist in the internalization assay. The super-agonist effect suggests that SNC-80 may lead to higher levels of internalized receptor, and subsequently lower levels of receptor reserve – thus behaving as a “functional antagonist.”
Monitor RTK Internalization through Ligand or Receptor Antibody Activation
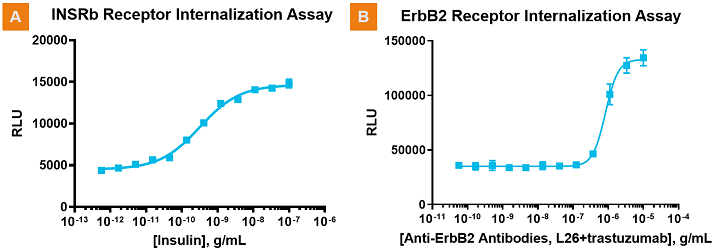
Monitor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) internalization through ligand or receptor antibody activation. A. Insulin receptor b (INSRb) internalization in response to incubation with increasing insulin concentrations. B. Epidermal growth factor B2 (ErbB2) receptor internalization is detected when cells are incubated with two different ErbB2 antibodies, including the therapeutic antibody trastuzumab (Herceptin®). Similar robust ErbB2 internalization was observed when cells were incubated with Herceptin and pertuzumab (Perjeta®; data not shown). Herceptin and Perjeta are registered trademarks of Genentech USA, Inc.
Study Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) – Analyze Antibodies That Activate Checkpoint Receptor Internalization
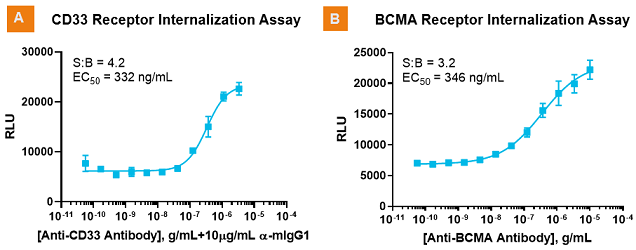
Checkpoint receptor antibodies activate receptor internalization. A. PathHunter internalization assay for the CD33 checkpoint receptor was tested with a commercial antibody to CD33. CD33 antibody was pre-incubated with a secondary antibody to cluster the CD33 receptor and then added to cells to monitor internalization. With higher cross-linked antibody concentrations, greater amounts of PK-tagged CD33 complemented EA-tagged protein localized to the endosome. A number of ADCs for CD33 are in clinical trials for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. B. B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) receptor internalization was activated with a commercial BCMA antibody. Several BCMA ADCs are in development as a therapeutic for multiple myeloma.
Measure Activation and Translocation of NHRs from the Cytoplasm to the Nucleus
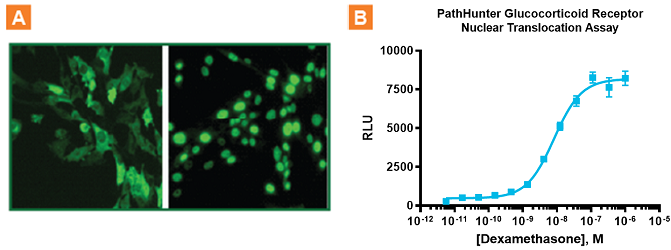
Quantitative data showing binding and ligand-induced translocation on NHRs such as androgen, glucocorticoid, liver X, mineralcorticoid, and progesterone receptors. Monitoring Glucocorticoid Receptor Nuclear Translocation. A. Immunofluorescence analysis of dexamethasone induced Glucocorticoid Receptor translocation into the nucleus using PathHunter CHO-K1 Glucocorticoid Receptor Nuclear Translocation cells. B. Translocation EFC-based assay (Cat. No. 93-0002C2) of the same cells stimulated with dexamethasone for 3 hours and results shown an EC50 of 8.2 nM and excellent signal-to-background of 15.9. PathHunter NHR translocation assays employ full length NHRs providing more biologically relevant data, and shorter assay times allowing for fewer off-target effects.
Both multi- and single-pass membrane receptors constitutively exhibit complicated and dynamic membrane receptor trafficking as well as internalization induced by…
Read MoreDiscoveRx offers an industry-leading portfolio of over 600 naturally coupled human and ortholog G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) cell lines designed…
Read MoreGPCR activation results in G-protein dependent events such as second messenger signaling, as well as initiation of a host of…
Read MoreThe pattern of intracellular signaling downstream of GPCR activation is now known to be specific to the ligand-receptor pair as…
Read MoreCompounds that bind to allosteric sites offer many benefits over those which interact orthosterically. These include enhanced specificity, ability to…
Read MoreThe recent appreciation of functional selectivity/ligand bias in GPCR signaling has uncovered new opportunities for therapeutic discovery and continues to…
Read MoreDiscoveRx® has pioneered a novel enzyme complementation system to monitor cellular events such as protein translocation, protein interactions, and degradation…
Read MoreDiscoveRx® has pioneered a novel enzyme complementation system to monitor cellular events such as protein translocation, protein interactions, and degradation…
Read MoreCystic fibrosis (CF) patients have mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) chloride channel that result in reduced…
Read MoreDiscoveRx has pioneered a novel enzyme complementation system to monitor cellular events such as protein translocation, protein interactions, and degradation…
Read MoreThere is an increasing need to generate therapeutics targeting metabolic and gastrointestinal diseases to address the global burden of metabolic…
Read MoreListen to the US PEGS 2023 conference talk by Venkatesh Chari, Ph.D. on MOA-reflective, functional cell-based assays (cell lines and…
Watch NowLearn about PathHunter Internalization assays developed to measure translocation of both single-pass and multi-pass receptors (like RTKs, checkpoint receptors and…
Watch NowLearn about PathHunter pharmacotrafficking assays to identify small molecule compounds that rescue disease relevant mutant membrane proteins like GPCRs, ion…
Watch NowLearn about Eurofins DiscoverX cell line engineering, assay development, and recombinant enzyme production custom capabilities. Find out more about cell…
Watch NowThe webinar addresses the challenge that much of the GPCR druggable space remains untapped for potential therapeutic targets. To address…
Watch NowExplore Functional Systems Driving GPCRs to the Forefront of Focused & Safe Therapeutics. Gain insights from industry experts on GPCR…
Read MoreAs more is learned about the intricacies of GPCR signaling, the harder it becomes to accurately describe ligand activity using…
Read MoreHere we show how PathHunter GPCR Internalization assays can be used to differentiate between strongly internalizing and weakly internalizing agonist…
Read MoreAs more is learned about the intricacies of GPCR signaling, the harder it becomes to accurately describe ligand activity using…
Read MoreVenkatesh Chari, Ph.D. Scientific Market Development Manager Eurofins DiscoverX Products LLC
Read MoreCell-based assays are useful for understanding cellular pathways; characterizing targets and their function; identifying, screening, and optimizing ligands or drugs…
Read MoreTranslocation and Trafficking of Membrane Proteins
Read MoreExplore GPCR-Ligand Interactions & Signaling Pathways with Binding & Functional Assays
Read MoreAs more is learned about the intricacies of GPCR signaling, the harder it becomes to accurately describe ligand activity using…
Read MoreProducts & Custom Development Capabilities.
Read MoreExplore GPCR-Ligand Interactions & Signaling Pathways with Binding & Functional Assays
Read MoreComprehensive Eurofins DiscoverX product list to enable your drug discovery and development programs focused on checkpoint receptors, cytokine receptors/interleukins, cytotoxicity,…
Read MoreYour source for a complete offering of GPCR assays, cell lines, and membrane preps
Read MoreG-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have varying and diverse physiological roles, transmitting signals from a range of stimuli, including light, chemicals, peptides,…
Read MoreG-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have varying and diverse physiological roles, transmitting signals from a range of stimuli, including light, chemicals, peptides,…
Read MoreType 2 diabetes (T2D) affects Latinos at twice the rate seen in populations of European descent. We recently identified a…
Read More
Accelerate cancer immunotherapy drug development with easy-to-use, functional cell-based assays
Read More
Cell-based assays to measure 2nd messengers (cAMP & calcium), β-arrestin recruitment, receptor internalization, & ligand binding
Read More
Non-imaging, cell-based internalization assays for screening & identifying safer drugs for GPCRs
Read More
Cell-based assays to evaluate activation & translocation of nuclear proteins including nuclear hormone receptors
Read More
Quantitative cell-based assays to identify pharmacochaperones that stabilize & correct disease-relevant mutant GPCRs, ion channels, or transporters
Read More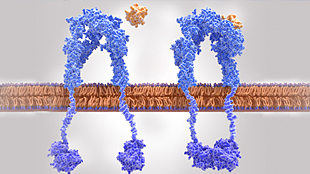
Functional & activity assays to analyze receptor dimerization, phosphorylation, internalization, & SH2-recruitment of RTKs & CTK/cytokine receptors
Read More
Simple, orthogonal reporter-based assays for screening & understanding therapeutic MOAs
Read More
Complete set of parental cell lines, vectors, kits, & retroparticles to build your own stable cell lines & cell-based assays
Read More
Custom cell lines, kits, assays, & protein development capabilities optimized to fit your requirements
Read More
