Nuclear Protein Product Solutions
Cell-based Assays to Evaluate Activation and Translocation of Nuclear Proteins
Nuclear proteins are key targets for drug development due to their ubiquitous roles in controlling cellular behavior and pathway expression. The translocation of many nuclear proteins into and out of the nucleus is a highly controlled mechanism that can dictate protein function. Controlling this translocation behavior using therapeutics, or ensuring that a potential drug does not cause undesired effects on translocation, are important applications for measuring nuclear translocation.
Nuclear hormone receptors (NHRs), including steroid receptors, are a critical subset of nuclear proteins that regulate gene expression in response to ligand activation and are intimately involved in endocrine pathway signaling. NHRs commonly rely on a coactivator or corepressor protein, often a steroid receptor cofactor (SRC protein), to perform their function. Enhancing or disrupting the association of these proteins can be a target for therapeutic development focused on controlling NHR-related gene expression.
Eurofins DiscoverX® provides PathHunter® nuclear translocation and protein interaction cell-based, functional assays to investigate protein translocation events and activation of nuclear proteins. Nuclear translocation assays allow for studying the trafficking of your protein of interest to and from the nucleus and analyzing the pharmacological effects of therapeutics on these events. Protein interaction assays can be used to evaluate the interaction of NHRs and their cofactors, including therapeutics that affect this protein-protein interaction.
Among the advantages of the Eurofins DiscoverX platform is that, unlike other assays, these cell-based assays do not require antibodies, fluorescent tags, or specialized equipment, and they provide an easy-to-use, high-throughput capable, and quantitative measurement of protein-protein interaction.
Product Highlights
- Homogeneous, HTS-compatible Assay – An easy-to-use, sensitive, and high-throughput cell-based assay platform without the need for antibodies, fluorescent tags, or specialized equipment
- Flexible Solutions – Create your own quantitative, functional cell-based assays to study nuclear translocation of any desired target protein
- Diverse Therapeutic Discovery – Quantify small molecules, peptides, or antibody-based therapeutics targeting nuclear proteins
- Nuclear Translocation Cell Lines and Assay Ready Kits
- Nuclear Protein Interaction Cell Lines
PathHunter nuclear protein assays are based on the proprietary Enzyme Fragment Complementation (EFC) technology to measure the movement of proteins into the nucleus or the protein-protein interactions in the nucleus.
NHR Nuclear Translocation Assay Principle
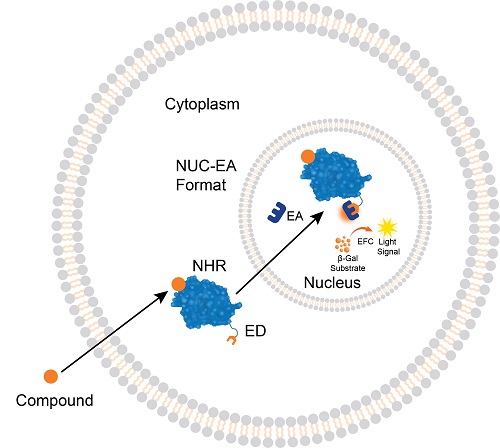
NHR translocation assays detect the binding of small molecules that trigger NHR activation and translocation into the nucleus. The cells have been engineered to express the ED fragment of the β-gal enzyme fused to the NHR (that is located in the cytoplasm) and the EA fragment localized in the nucleus. Ligand binding to the NHR induces the receptor translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, forcing the complementation of the ED and EA fragments and the formation of an active β-gal enzyme. The enzyme then hydrolyzes a substrate to generate a chemiluminescent signal that can be easily measured on any standard luminometer.
Nuclear Protein Translocation Assay Principles
Nuclear protein translocation assays allow for the identification, screening, lead optimization, and even safety testing of therapeutics. These assays monitor the activation or inhibition of a particular signaling pathway coupled with the movement of proteins from the cytosolic compartment to the nuclear compartment. In general, this approach enables you to create a highly specific, non-transcriptional assay for almost any protein that is known to translocate to the nucleus, such as FOXO3, NRF2, XBP1, p53, and many others. Learn about several translocation assays on the nuclear proteins and signaling pathways pages.
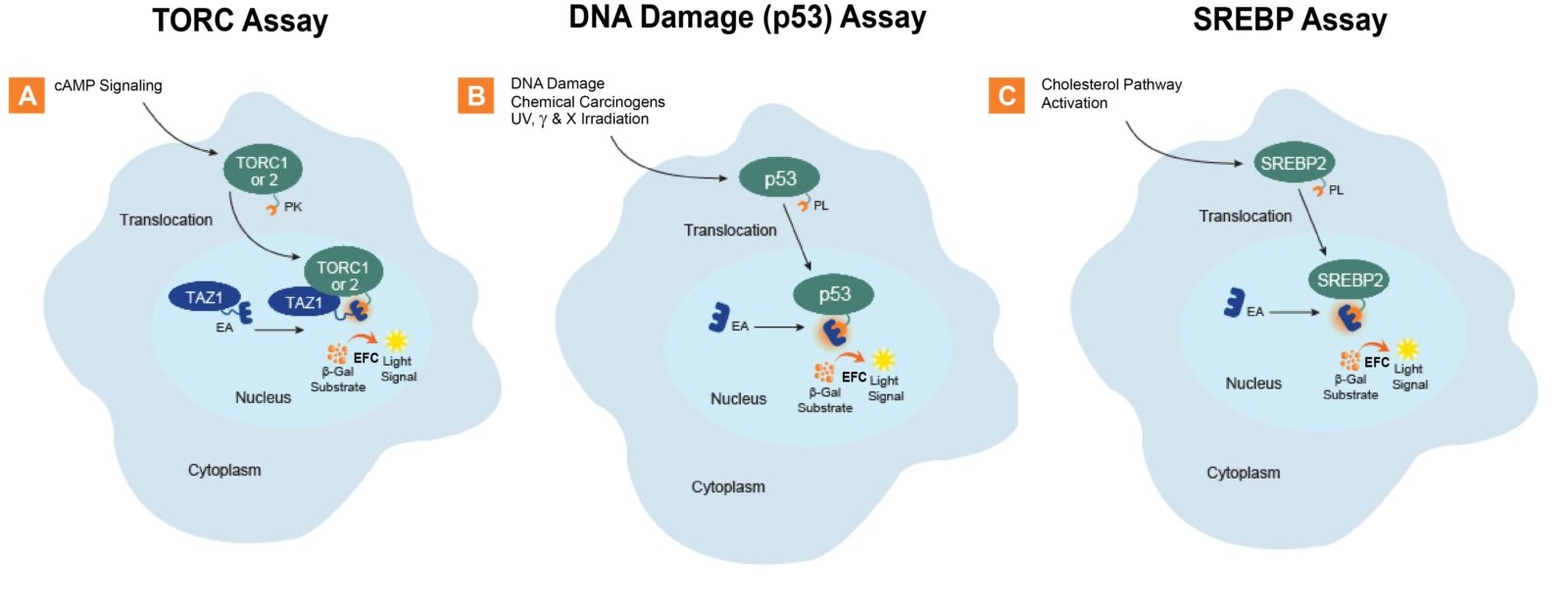
Nuclear translocation assays allow for the identification, screening, lead optimization, and safety testing of therapeutics. These assays monitor the activation or inhibition of a particular signaling pathway coupled with the movement of proteins from the cytosolic compartment to the nuclear compartment. In general, this approach enables you to create a highly specific, non-transcriptional assay for almost any protein that is known to translocate to the nucleus, such as FOXO3, NRF2, XBP1, p53 and many others. Example PathHunter signaling pathway assays shown here measure (A.) TORC1 or TORC2, (B.) p53, and (C.) SREBP2 translocation from the cytosol to the nucleus. The cell lines have been engineered to express the two complementing EFC β-galactosidase (β-gal) fragments within different cellular compartments. The translocating protein is tagged with the small EFC enzyme donor (ED) fragment, while the larger EFC enzyme acceptor (EA) fragment is located in the nucleus. Activation of the pathway by a ligand (small molecule, peptide, or biologic) triggers the ED-tagged protein that is being measured to translocate to the nucleus and complement with the EA to form a fully active β-gal enzyme. The enzyme then hydrolyzes a substrate to generate a chemiluminescent signal that can be easily measured on any standard luminescence reader.
NHR Protein Interaction Assay Principle
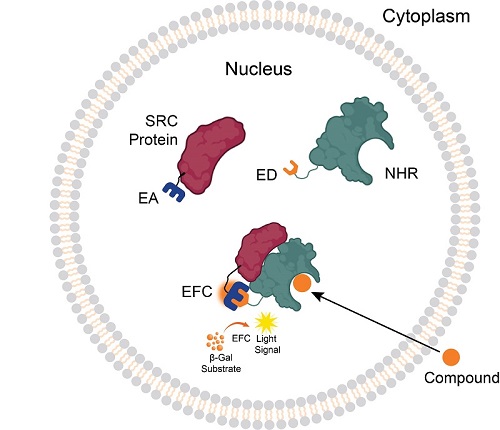
NHR protein interaction assays detect the association of the NHR with a coactivator or corepressor accessory protein. The cells have been engineered to express the ED fragment of the β-gal enzyme fused to the NHR (that is located in the nucleus), and the EA fragment fused to the accessory protein (SRC protein). When the NHR is engaged by its small molecule ligand, it forms a complex with the accessory protein, forcing complementation of the ED and EA fragments and creating active β-gal. When provided with a substrate, a chemiluminescent signal is produced.
Measure Activation and Resulting Nuclear Translocation of Transcription Factors

Activation-induced nuclear translocation of transcription factors. PathHunter nuclear translocation cells (Cat. No. 93-0876C3) expressing FOXO3 (Forkhead Box O3; transcription factor) were stimulated with wortmannin for 2 hours leading to the translocation of FOXO3 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. EC50 of 13.8 nM and signal-to-background (S:B) of 6.7.
Measure Activation-Induced Nuclear Translocation of Transcription Factors
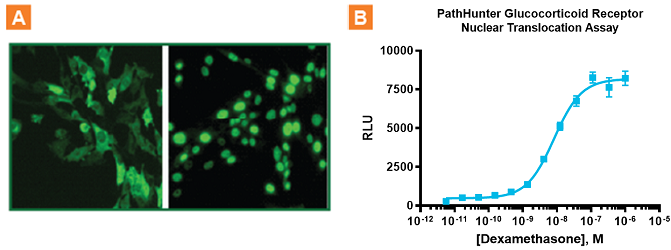
Quantitative data showing binding and ligand-induced translocation on NHRs such as androgen, glucocorticoid, liver X, mineralcorticoid, and progesterone receptors. Monitoring Glucocorticoid Receptor Nuclear Translocation. A. Immunofluorescence analysis of dexamethasone induced Glucocorticoid Receptor translocation into the nucleus using PathHunter CHO-K1 Glucocorticoid Receptor Nuclear Translocation cells. B. Translocation EFC-based assay (Cat. No. 93-0002C2) of the same cells stimulated with dexamethasone for 3 hours and results shown an EC50 of 8.2 nM and excellent signal-to-background of 15.9. PathHunter NHR translocation assays employ full length NHRs providing more biologically relevant data, and shorter assay times allowing for fewer off-target effects.
Measure Ligand-Induced Association of NHRs with their Accessory Proteins
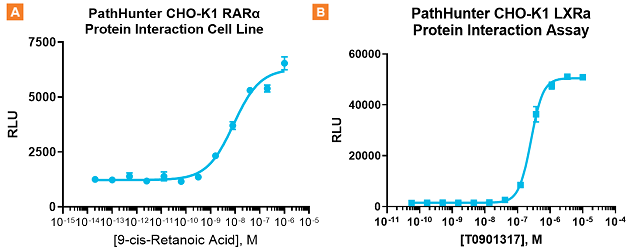
Obtain quantitative data showing ligand-induced protein interaction between NHRs and their accessory proteins. A. PathHunter RARα cells (Cat. No. 93-0325C2) were stimulated with 9-cis-Retanoic acid for 6 hours, which lead to the interaction of RARα with its accessory protein. EC50 of 8.5 nM and S:B of 5.2. B. PathHunter LXRα cells (Cat. No. 93-0389C2) were stimulated with T0901317 for 6 hours, which lead to the interaction of RARα with its accessory protein. EC50 of 257.2 nM and excellent S:B of 34.6.
Nuclear Translocation Assay Targets
| FOXO3 (PI3) | p53 | SREBP2 | TORC2 (CRTC2) | XBP1 |
| Keap1-NRF2 | RELA | TORC1 (CRTC1) | TORC3 (CRTC3) | β-Catenin (Wnt-FzGSK3β) |
NHR Nuclear Translocation and Protein Interaction Targets
Learn about Eurofins DiscoverX cell line engineering, assay development, and recombinant enzyme production custom capabilities. Find out more about cell…
Watch NowCell-based assays are useful for understanding cellular pathways; characterizing targets and their function; identifying, screening, and optimizing ligands or drugs…
Read MoreFunctional Cell-Based Assays, Cell Lines, & Proteins for Cancer Research Improved or novel small molecule or biologic therapeutics for cancer…
Read MoreRobust Cell-Based Assays to Identify Therapeutic Hits Rapidly
Read MoreProducts & Custom Development Capabilities.
Read MoreComprehensive Eurofins DiscoverX product list to enable your drug discovery and development programs focused on checkpoint receptors, cytokine receptors/interleukins, cytotoxicity,…
Read More
Simple, orthogonal reporter-based assays for screening & understanding therapeutic MOAs
Read More
Screening cell-based assays for analyzing the movement of proteins to multiple membrane compartments within the cell
Read More
Complete set of parental cell lines, vectors, kits, & retroparticles to build your own stable cell lines & cell-based assays
Read More
Custom cell lines, kits, assays, & protein development capabilities optimized to fit your requirements
Read More
